OL display on multimeter meaning and measuring
What does OL mean on a multimeter , this is the frequency ask question from digital multimeter user. It has many meaning , it depends on what is the test function range that you set. I have researched from many multimeter manual and found that OL = Over a range Limit and other detail at measuring explaination when LCD display " OL" mean Over Range and it suggest user to change the range to higher range or seek the appropriate range for the measured amount. For example when you measure 9VDC battery and use 0.000V range by manual selection , the testing result display OL as photo , it mean this range selected is not suitable for 9VDC and you have to change setting to higher range. OL display also displays with other test function range such as resistor measurement , current measurement , capacitor test , temperature measurement etc. View photo below for more understanding.
OL display , measuring example for range selection is not suitable.
It displays 9.43V as it should be (mean 00.00 DC voltage range is suitable for 9VDC )
The good measurement , you have to select the right range and right test function before operating any measuring. Unknown value it suggest to chose the highest range first. For advance multimeter it has auto range , but , for low cost multimeter has only manual range selection and user need to study how to set the suitable range for the target measurement.
OL display when testing condition of components = not shorted , not connected.
The other meaning of OL display on test function such as diode test , continuity check . It indicates the condition of component "good" or " bad" , defective. OL display for diode check , In case of reverse bias it means diode is not shorted , 2 terminal is not connected and when supply reverse bias to diode it has to display "OL" as it should be = good diode. Example will be shown by photo.
Forward bias to a diode , it displays 0.3-08V = good diode.
Reverse bias to a diode , it displays OL = good diode and this time OL mean "not shorted "
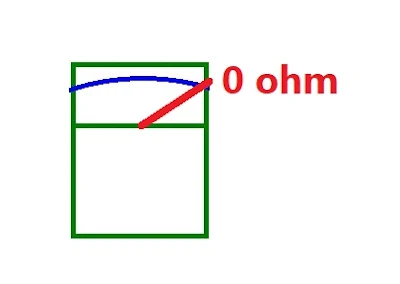
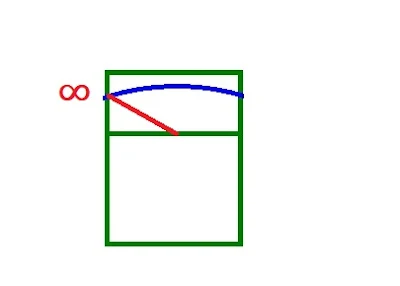
OL display when we use continuity check. When checking switch at OFF position it has to be not connected , not shorted condition. This time OL display mean contact is not shored (good contact). Technical term NO terminal ( Normally open) it mean contact is not connected and the testing result get " not connected " as it should be. When changing the switch position to "ON" it means internal contact is connected or shored , the display should be 0 ohm for good contact. If the display still show OL it means internal contact is not connected as it should be condition , so OL = bad contact.
ON position , the internal contact is connected , but , multimeter display OL means internal contact is not connected as it should be so this case it is a bad switch contact.
Read more topics of testing , from here.